Why Magnetic Core Material Plays a Crucial Role in Inductor Performance: A Deep Dive
Nov 20, 2025
Now fast-paced world of electronics, engineers are constantly faced with the challenge of optimizing circuit performance while maintaining compactness and energy efficiency. One crucial, yet often overlooked, component in these designs is the magnetic core used in inductors. The material of the magnetic core can dramatically influence the inductor’s performance, particularly in high-frequency applications.
This blog will explore how different magnetic core materials impact inductor performance, why choosing the right material is critical, and how these materials affect the efficiency and longevity of your electronic devices.
The Importance of Magnetic Core Material
Magnetic cores play a vital role in the function of inductors. They influence inductance, energy storage, efficiency, and power losses. The performance of an inductor is highly dependent on the magnetic material it’s made from, and the right choice of material can make a significant difference in how well the device operates across different frequencies and power levels.
There are several materials commonly used for magnetic cores in inductors, such as ferrite, silicon steel, and nanocrystalline alloys. Each material comes with its own set of advantages and limitations, making it essential for engineers to understand the material properties in order to make the right choice for a given application.
How Different Magnetic Core Materials Affect Performance
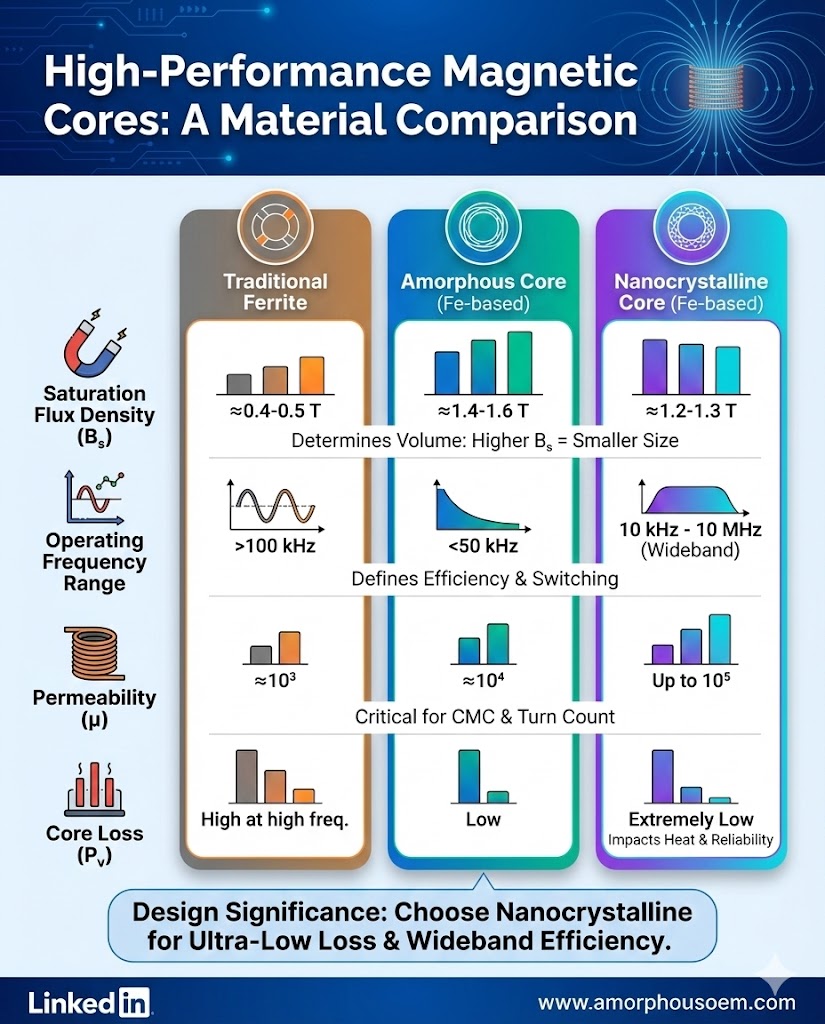
Mn-Zn Ferrite CoresFerrite cores are made from iron oxide combined with other metals, and they are widely used in high-frequency applications like switch-mode power supplies and transformers. They offer relatively low eddy current losses at high frequencies, making them suitable for circuits operating in the kilohertz (kHz) to megahertz (MHz) range. Additionally, ferrite cores have high magnetic permeability, which means they can store more magnetic energy with relatively low losses, improving circuit efficiency.
However, Mn-Zn ferrite cores have limitations at very high frequencies, where losses can increase due to core material saturation. Ferrite cores are also less efficient at very low frequencies, which makes them less suitable for power transformers or circuits that require low-frequency performance.
Nanocrystalline CoresNanocrystalline cores, a newer material in magnetic technology, offer exceptional performance in high-frequency applications. These cores are made from iron and other elements arranged in a nanocrystalline structure, which allows them to exhibit significantly higher magnetic permeability compared to ferrite cores.
Nanocrystalline cores provide lower losses and higher efficiency in high-frequency circuits, such as power inductors in high-frequency switching power supplies. Their higher saturation flux density makes them particularly useful for high-power applications, where maintaining performance at higher current levels is essential.
The main advantage of nanocrystalline cores over ferrite is their ability to operate with up to 30% lower high-frequency losses. They also maintain low hysteresis losses even at very high frequencies (several hundred kHz), making them ideal for applications in the 5G telecommunications, electric vehicles (EVs), and data centers.
Silicon Steel CoresSilicon steel is another material that has been used for decades in power transformers and other low-frequency applications. Its relatively low magnetic losses make it suitable for power transformers operating at 50-60Hz in traditional power grids.
However, silicon steel’s performance at higher frequencies is limited due to significant eddy current losses. This makes it less suitable for high-frequency applications, such as modern power electronics or devices that operate in the kHz-MHz range.
The Mechanism Behind Magnetic Core Performance
The performance of magnetic cores in inductors is largely determined by the following factors:
Magnetic Permeability: The ability of a material to support the formation of a magnetic field. Higher permeability means better energy storage capacity and lower losses.
Hysteresis Losses: The energy lost when the magnetic material is magnetized and demagnetized. Materials with lower hysteresis losses are more efficient.
Eddy Current Losses: Induced currents within the core material that cause heat loss. High-frequency applications require materials that minimize these losses.
Saturation Flux Density: The maximum magnetic field strength the material can handle before its magnetic properties break down. A higher saturation flux density means the material can handle higher currents without losing performance.
Quantifying the Performance Gains
Nanocrystalline materials reduce high-frequency losses by up to 30% compared to Mn-zn ferrite cores.
They also provide 2-3 times higher permeability, which means more efficient energy storage and enhanced inductor performance in high-power, high-frequency applications.
These materials are particularly useful in systems requiring low hysteresis loss and high-frequency operation (several hundred kHz), which are essential in modern electronics like switch-mode power supplies, 5G networks, and electric vehicles (EVs).
Choosing the Right Core Material for Different Applications
When selecting a magnetic core for an inductor, engineers must consider the specific requirements of the application:
Switch-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS): Ferrite and nanocrystalline cores are ideal for high-frequency operation and minimizing losses.
Electric Vehicles (EV): Nanocrystalline cores, with their high saturation flux density and low losses, are essential for handling large currents in high-power applications.
5G Networks: High-performance cores, such as nanocrystalline, offer superior efficiency for handling high-frequency signals while minimizing power loss.
Data Centers: For high-speed communication and efficient power conversion, nanocrystalline cores are increasingly being used to improve system efficiency.
The Critical Role of Magnetic Core Material in Inductor Design
Magnetic core material plays a critical role in the performance of inductors and the overall efficiency of electronic circuits. By selecting the appropriate core material—whether it’s ferrite, nanocrystalline, or silicon steel—engineers can ensure that inductors function efficiently across different frequencies and power levels.
Understanding the benefits and limitations of each material is essential for optimizing circuit designs in today’s high-performance, energy-efficient electronic systems. As technologies like 5G, electric vehicles, and AI data centers continue to evolve, the importance of choosing the right magnetic core material will only grow.
What’s Your Biggest Challenge in High-Frequency Inductor Design?
In the fast-evolving world of electronics, engineers are continuously tasked with pushing the limits of technology. Whether you’re designing power supplies, communication systems, or next-gen EVs, understanding the relationship between magnetic core material and inductor performance is key to achieving optimal results.
Let us know your thoughts, DM us.
Read More